5 Steps to Build a Multilingual WordPress Site Without Plugins

Building a multilingual WordPress site in 2024 without using plugins can be effectively achieved through WordPress Multisite. WordPress Multisite allows you to create a network of individual WordPress sites, each in a different language but connected by a single WordPress core. This setup eliminates the need for multiple WordPress configurations for each language.
If there’s a potential multilingual market for your business, and your competitors aren’t taking advantage of that, you definitely need to go for it!
Table Of Content
Building a Multilingual WordPress Website: Advantages and Strategies
1. Why Go for a Multilingual Website?
In today’s globalized world, creating a multilingual WordPress website opens doors to broader markets and diverse audiences. Businesses can tap into new regions, catering to customers in their native languages. This approach not only broadens reach but also resonates more personally with potential clients, enhancing brand presence across different cultures.
2. Top 2 Methods for creating multilingual websites?
Here’s a more detailed look at the two most adopted methods in 2024 for creating a multilingual WordPress website:
- WordPress Multisite:
- Overview: WordPress Multisite allows for the creation of a network of sites under a single WordPress installation, where each site can be configured in a different language.
- Setup Process: To set up a Multisite, you need to enable Multisite in your wp-config.php file, set up a network, and configure network settings. Each site within the network can then be assigned a different language, either using subdomains (like fr.yoursite.com) or subdirectories (yoursite.com/fr).
- Pros:
- Centralized Administration: Manage multiple sites from a single dashboard.
- Shared Resources: Themes and plugins can be shared across the network, reducing redundancy.
- Scalability: Easily add new languages as new sites within the network.
- Cons:
- Technical Complexity: Requires a good understanding of WordPress and possibly some coding knowledge.
- Maintenance: Each site needs to be updated and managed individually, which can be time-consuming.
- Hosting Requirements: May require more robust hosting solutions to handle multiple sites efficiently.
- Using Translation Plugins (such as TranslatePress, WPML, Weglot):
- Overview: These plugins allow you to manage and translate content within your WordPress site. They support automatic translation and provide tools for manual adjustments.
- Functionality: After installing the plugin, you can translate pages, posts, and even theme and plugin texts. Some plugins also offer advanced features like translation memory, integration with professional translation services, and support for RTL (Right-to-Left) languages.
- Pros:
- User-Friendly: Generally easy to set up and use, even for non-technical users.
- Seamless Integration: Works well with existing WordPress themes and plugins.
- Flexibility: Offers both automatic and manual translation options.
- Cons:
- Dependence on Third-Party Services: Subject to the reliability and limitations of the plugin.
- Translation Quality: Automatic translations may not always be contextually accurate.
- Performance Impact: Can increase website load times due to additional scripts.
In the upcoming sections of this article, we will delve deeper into the WordPress Multisite method, providing step-by-step guidance on how to effectively set up and manage a multilingual website using this approach.
3. Advantages of a Multilingual WordPress Site
- SEO Advantages:
- Increased Content for SERPs: Translating your content into multiple languages can result in more content indexed by search engines, potentially increasing organic traffic significantly.
- Reduced Competition: Non-English languages often face less competition in search engines, offering easier ranking opportunities.
- Localized SEO: Employing local SEO practices for each language can enhance reach in targeted regions.
- User Experience (UX) Advantages:
- Improved Conversion Rates: A multilingual site can lead to better user engagement, lower bounce rates, and higher conversion rates.
- Cultural Relevance: Localizing content beyond mere translation, such as adapting to cultural norms and holidays, resonates better with the audience.
- Accessibility: Offering content in native languages enhances accessibility and inclusivity, catering to a wider audience.
- Trust and Credibility:
- Native Language Communication: Communicating in a customer’s native language builds trust and credibility, as it reflects respect and understanding of their culture.
- Global Reach and Local Connection: While English is widely used, catering to native languages of various regions can significantly enhance a brand’s global appeal and local connection.
Steps to Build a Multilingual WordPress Site using Multisite
WordPress Multisite enables the creation of multiple sites under the same installation. You can add different languages as individual sites within this network. In this section, you’ll learn how to create your own multilingual WordPress site without plugins…from scratch!
1. Set up and create a WordPress Multisite with Subdomains:
Activating Multisite on a Fresh WordPress Installation
Activating Multisite when you install WordPress involves a few extra steps. Firstly, you need to install WordPress and allowing a network.
- Open your
wp-config.php
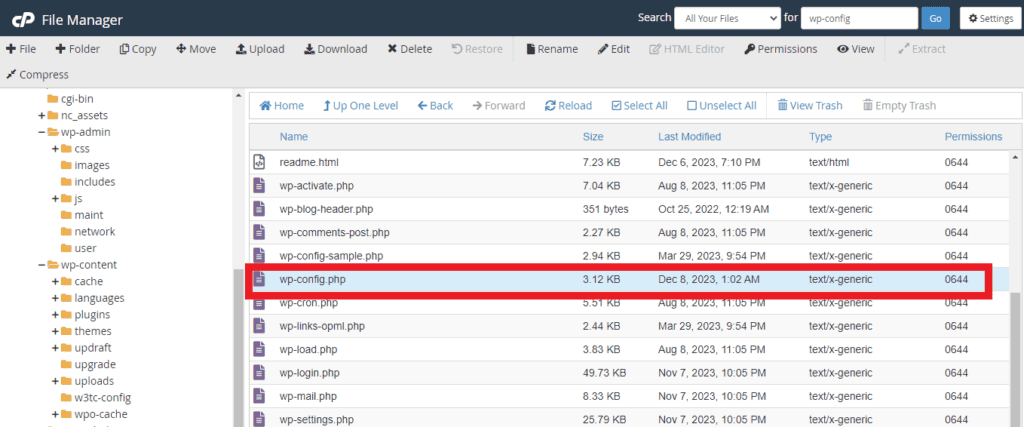
2. Above the line /* That’s all, stop editing! Happy blogging. */, paste this code :
define( 'WP_ALLOW_MULTISITE', true );3. Now save your wp-config.php file.
4. The next step is to visit the WordPress admin dashboard and go to Tools >Network Setup. You’ll be prompted to choose subdomains or subdirectories for your installation: choose the one that works for your network.
5. Edit the title of your network and email address of the network administrator when prompted, or leave them as they are. Click the Install Button.
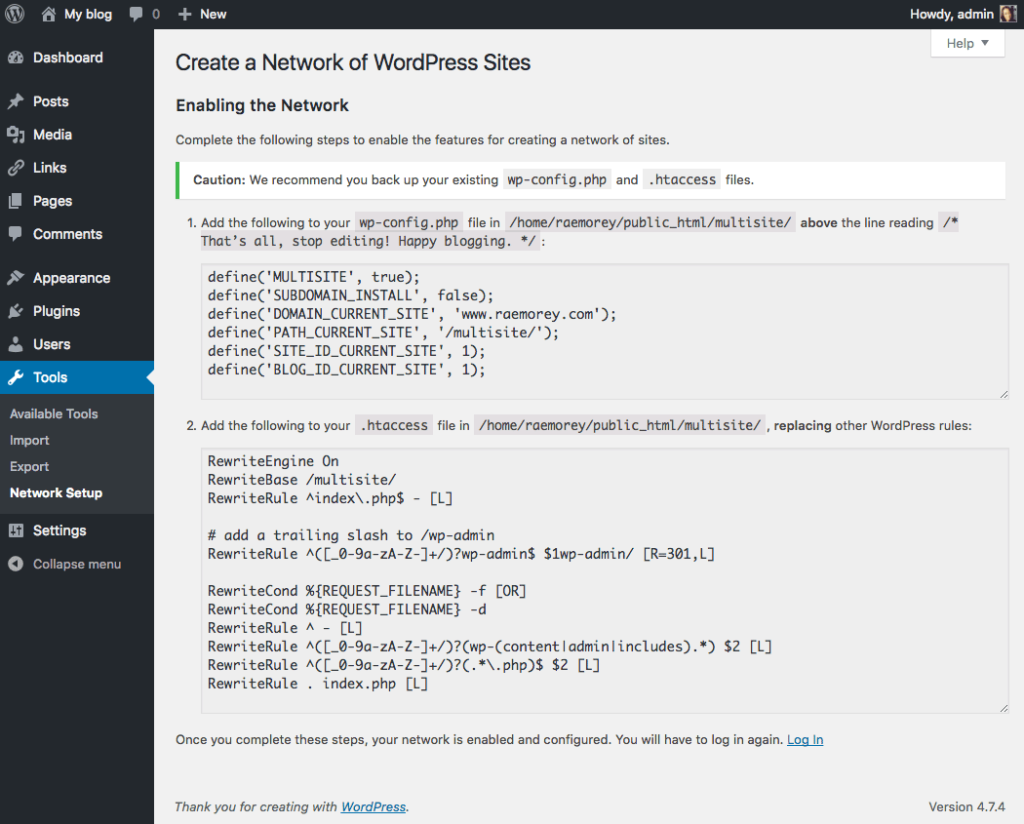
6. The final step is to copy some code provided by WordPress into your wp-config.php and .htaccess files.
You will be taken to the Network Install screen:
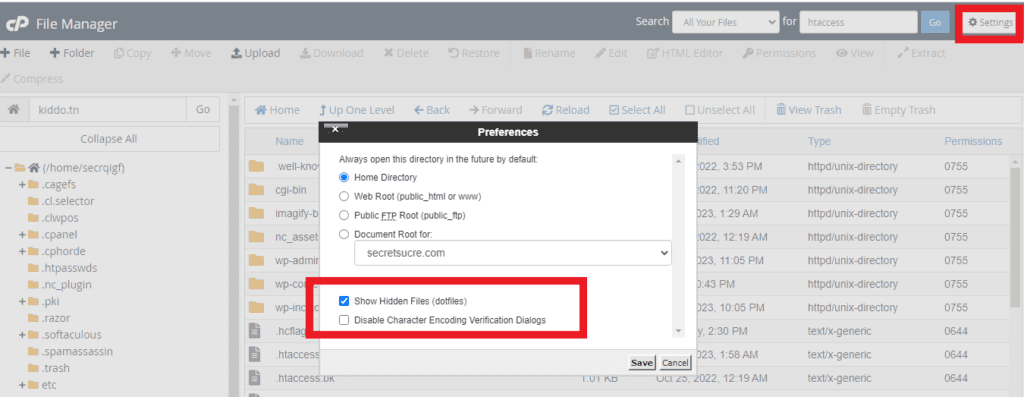
You can find the .htaccess file in the root directory of your web hosting. Access it via FTP using clients like Total Commander, WinSCP, or FileZilla. If it’s not immediately visible, ensure your FTP client is set to display hidden files.
One more easy way is to do it via your Hosting panel / Cpanel by going to Settings > Check show Hidden Files.
WordPress Multisite will now be installed. You’ll need to log in again, and when you do so you’ll see the Multisite dashboard.
Now you can start adding sites, plugins, themes and more.
Activating Multisite on an Established WordPress Installation
Follow the same steps as above with one exception: you won’t be given the option to select subdomains or subdirectories. If your site has been in existence for more than a month, you’ll be forced to use subdomains.
WordPress Multisite enables the creation of multiple sites under the same installation. You can add different languages as individual sites within this network
2. Set Up Subdomains for Each Language:
Create a subdomain for each language by going to My Sites > Network Admin > Sites, and selecting Add New..
Choose a subdomain for your new site. If you’re making a multilingual WordPress site, it makes sense to have the subdomain be the language code (e.g. dk for Denmark), but you can make it whatever you want.
Be careful not to change the Site Language option here. This will only change the language of your admin dashboard.
Once you’ve added the site, you’ll see it in the My Sites drop-down menu. You can manage it the same way you do the other by adding plugins, themes, and content.
3. Install Your Theme and Add Content:
Ensure that each site in your Multisite network uses the same theme, brand colors, and layout. This consistency is crucial for a cohesive user experience across different language versions
4. Translate Your Content
Use professional translators for accuracy and cultural sensitivity. Machine translations often lack the nuance and detail needed for effective communication
5. Configure Custom Menus
Create a custom menu for your main site, linking to the various language versions. This allows users to easily switch between languages.
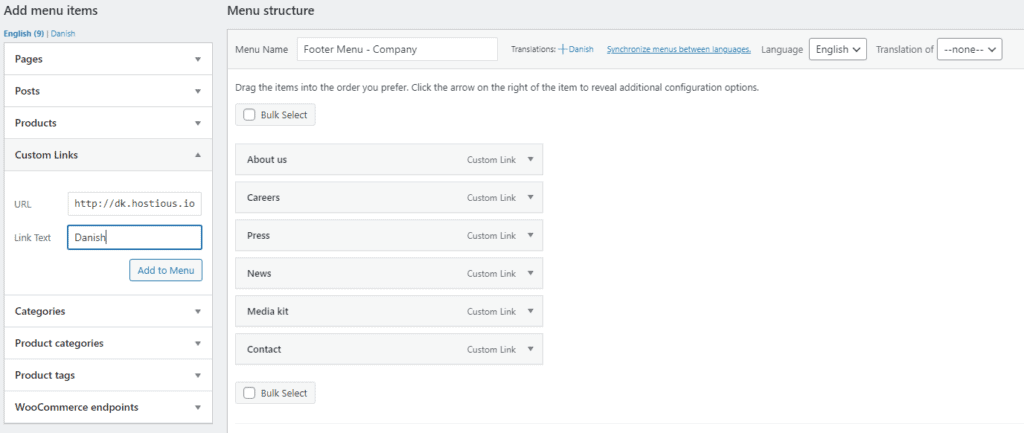
To create a custom link within your website’s primary menu, go to Appearance > Menus, and then edit your main menu.
Under Custom Links, enter the URL of the subdomain and the navigation label. Now add the custom link to the menu via the Add to Menu button.
12 Best Practices for a Multilingual WordPress Site
- Understand Your Audience: Use analytics tools to identify the languages most relevant to your audience. Focus on languages with high engagement and economic potential.
- Localize Content: Adapt your content to fit local cultural norms, holidays, and references. Localization increases relevance and engagement.
- Separate SEO Strategies: Each language version should have its own SEO strategy, with localized keywords and content.
- Use Hreflang Tags: Essential for multilingual SEO, these tags help search engines understand the language and regional targeting of your pages.
- Optimize for Mobile: Ensure your multilingual site is mobile-friendly, adhering to Google’s mobile-first indexing best practices.
- Engage with Local Audiences on Social Media: This improves SEO and drives traffic to your site.
- Monitor Analytics: Track the performance of each language version to optimize further.
- Build Local Backlinks: Aim for backlinks from local websites to boost your SEO in different regions.
- Maintain a Consistent Brand Image: Ensure that your site’s design and messaging are uniform across all languages.
- Regular Content Updates: Keep all language versions up-to-date with relevant content and functioning links.
- Comply with Regional Laws: Make sure your site adheres to digital content, privacy, and consumer rights laws in each language region.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Choose visuals, colors, and images that are appropriate and sensitive to different cultures.
The control and flexibility afforded by a Multisite setup are unmatched, providing you with the autonomy to craft, refine, and display your multilingual content exactly as you envision.
The key advantage of avoiding multilingual plugins in favor of a Multisite setup lies in its robustness and control. Coupled with a custom menu, it seamlessly guides your readers to the appropriate language-specific subsites, ensuring a user-friendly and cohesive experience across your global audience.
Frequently Asked Questions About WordPress Security
1. What are the key steps to set up a multilingual WordPress site using Multisite?
First, enable Multisite in WordPress. Then create subdomains or subdirectories for each language. Configure each site within the network individually with its respective language settings. Lastly, consider manual translation or professional services for accurate content translation.
2. How do I manage translations across multiple sites in a WordPress Multisite setup?
You can manage translations by manually updating content on each site or by employing professional translation services to ensure linguistic accuracy and cultural relevance.
3. Can I switch between using subdomains and subdirectories in WordPress Multisite?
Yes, initially you might need to choose between subdomains or subdirectories, but later you can switch between them. Remember, switching might require adjustments in settings and DNS configurations.
4. What are the advantages of using WordPress Multisite over plugins for a multilingual website?
WordPress Multisite offers more control over each language site, allows for shared resources like themes and plugins, and provides centralized management. It’s more scalable for large, diverse websites compared to plugin-based solutions.
5. Are there any specific SEO considerations for multilingual sites on WordPress Multisite?
Yes, each site should have its SEO strategy tailored to its specific language and audience. This includes localized keyword research, unique meta tags, and ensuring cultural relevance in content to improve search engine visibility in different language markets.